We all know that KVM switches or extenders can support video signal transmission and you can easily enjoy a high-quality visual experience when the video is displayed on the monitor. An important feature you should know is that these KVM devices support EDID. However, what is EDID? Why is it important for video displaying? Follow us and read this simple guide to learn more about this standard.
What is EDID?
EDID, also known as Extended Display Identification Data, is a standard for display identification data developed by VESA. When the computer is connected to the monitor, the EDID information of the monitor can be sent to the computer through DDC (Display Data Channel). VESA defines the DDC standard, including DDC1, DDC2B, DDC2B+, etc. At present, DDC2B is commonly used to achieve EDID information transmission.
How does it work?
1. Connect the computer/server (source devices) to a monitor (display).
2. The monitor will send its data to the server or computer.
3. After receiving the EDID from the monitor, the computer/server will adjust its output settings (resolution, refresh rate, etc.) according to the capabilities of the monitor.
For example, the max resolution that your monitor can support is 1920 x 1080@60Hz, then the connected computer/server will receive this data and automatically output the optimum resolution 1920 x 1080@60Hz.
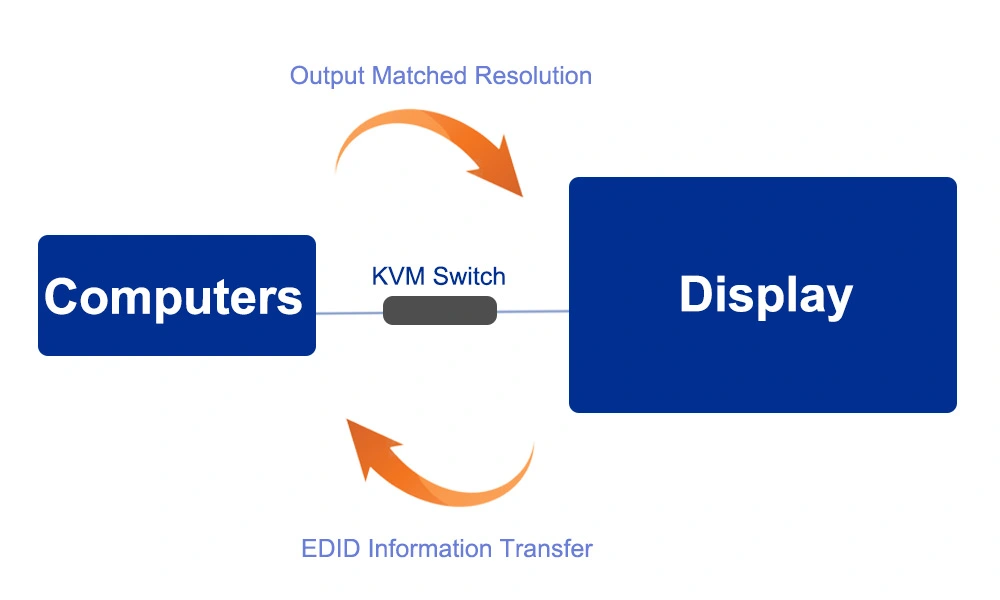
How about using a KVM switch or extender between the source device and the monitor?
KVM switches or extenders usually support EDID emulation, which allows them to emulate the important information of the monitor and send it to the computer/server. The EDID emulation function allows the KVM switch or extender to store extended display identification data so that the computer always outputs a fixed signal. For example, the KVM switch or extender forces the computer to output 4K signals.
Why EDID matters to KVM video transmission?
As we all know, there are many source devices and monitors with different specifications made by different manufacturers. This can easily lead to mismatched resolutions and black screens. To display the video clearly, the display device needs a uniform standard to communicate with the source device. Let us talk about its importance.
KVM switches and extenders are intermediate devices used to switch signals or extend the signal transmission. The importance of EDID emulation function in KVM video transmission includes:
- Resolution compatibility: KVM device with EDID emulation function can make the connected computer output suitable resolution that the monitor support to avoid compatibility issues.
- Flexible Configuration: The KVM devices can dynamically configure themselves based on the connected monitor when the source devices and monitors have different resolutions.
- Output optimization: The EDID emulation can optimize the output of connected computers or servers, providing users with an unmatched visual experience.
- Plug and Play: KVM switches can emulate consistent EDID data. This can make the connected computers “think” that they are always connected to a virtual display with consistent parameters. Users can add or remove computers directly and switch signals seamlessly.
What would happen if there is no EDID?
1. Mismatched resolutions: The computer possibly output a resolution that the monitor doesn’t support and then cause a black screen. The refresh rate error may cause latency.
2. Color and HDR anomalies: The color of the picture or video is not displayed correctly.
3. Stability issue: The lack of EDID may cause the video to display abnormally when users try to switch computers.
Conclusion
In short, EDID is a VESA standard used to make the computer automatically output optimum signals to ensure the screen is displayed correctly. It is important for KVM video transmission because it can achieve compatible resolutions, flexible configuration, output optimization, and a plug-and-play switching experience.



